What does A1C mean for me?
What A1C Is and Why It Matters
Your A1C reflects your average blood glucose (also known as blood sugar) level over the past two to three months. Your A1C level differs from the average you see on your blood glucose meter because it is a percentage and not a glucose value. Your blood glucose meter measures your blood sugar at certain moments, while your A1C is affected by all of your blood sugars over a period of time. The higher your A1C, the more at risk you are for developing diabetes-related complications. Ranges are as follows:

- Below 5.7% indicates normal average blood sugar levels
- 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes
For most adults with diabetes, <7% is a common A1C target. Consult your doctor for your personal A1C target number.
How A1C Relates to Self-Monitoring
Your A1C is just one of the numbers that will help you manage your diabetes. Remember, it is an average and will not show when blood sugar levels are high or low. Self-monitoring your blood sugar is key to helping you understand your A1C number and reach your diabetes health and wellness goals. Consult your doctor on how often and when you should test your blood sugar.
Regular self-monitoring helps you track whether you are in your target range and gives you a fuller picture of your blood sugar levels, helping you make your daily decisions about nutrition, exercise, and adjustment to medications like insulin, when necessary.
The chart below shows how multiple self-monitoring blood glucose checks over 4 days compare with an A1C measurement:
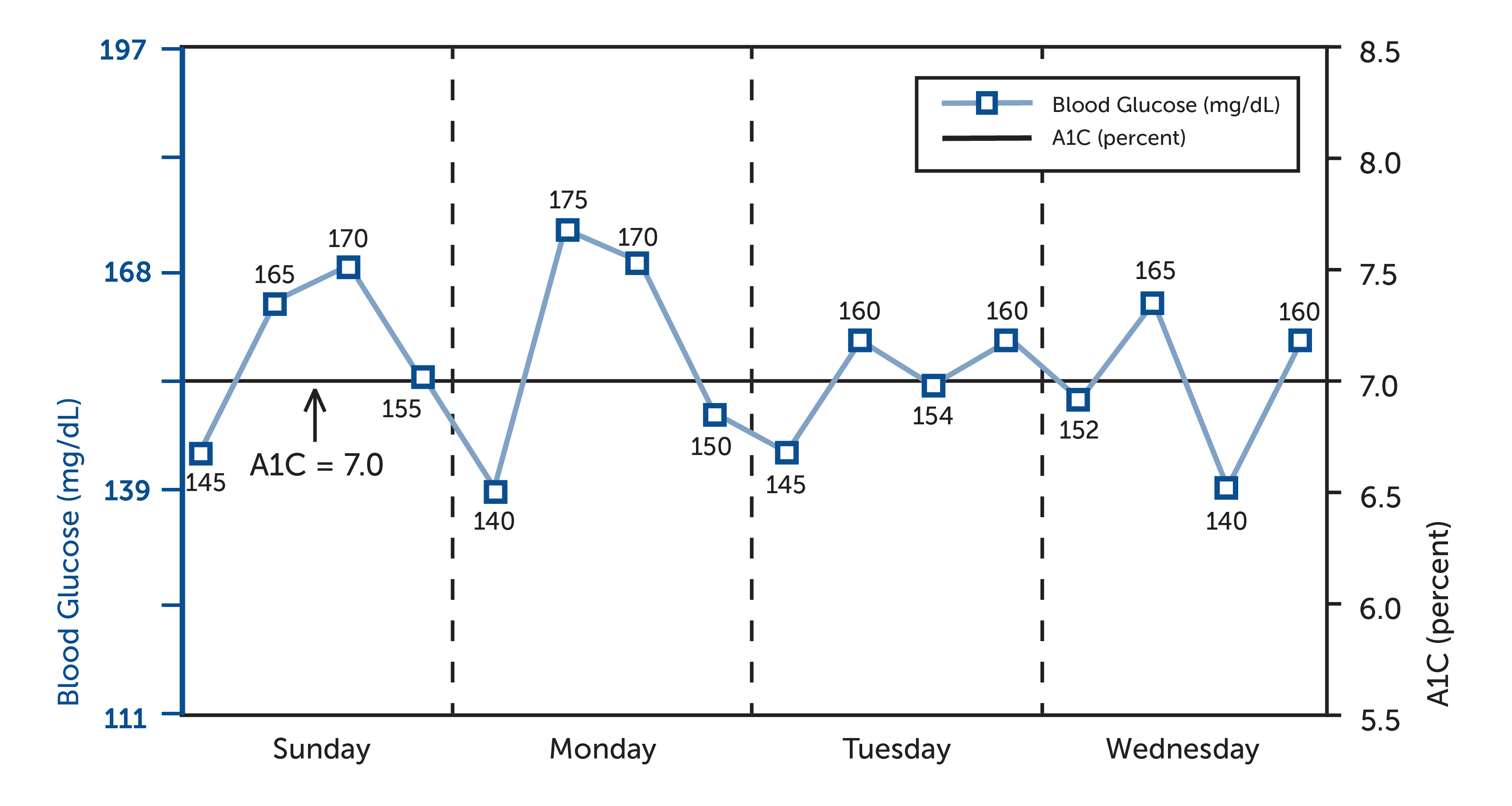
Blood glucose measurements were taken four times per day (pre-breakfast, pre-lunch, pre-dinner, and bedtime).
Note that the A1C reading reflects the average of all the blood glucose numbers, including the higher and lower numbers. The average masks the extremes. Your A1C reading is only one measurement that should be used when assessing your overall diabetes management goals. Self-monitoring your blood sugar is also key in your overall diabetes management plan.
Readings In Range
Consistent monitoring of your blood sugar levels can lead to a better A1C, which has been proven to produce better health benefits. With the A1C comparator on the OneTouch Reveal® mobile app, you can compare your lab A1C to the average of your blood sugar readings from your meter over the last 90 days.
Your Personal A1C Goal
Although studies show that lowering your A1C reduces the risks for diabetes complications, each person’s A1C goal should be personalized. Factors like diabetes history and your general health play a part in determining what your A1C goal should be. Consult your diabetes care specialist to determine your A1C goal.
Sources:
American Diabetes Association (ADA). Understanding A1C. Last accessed online April 29, 2022
Mayo Clinic. A1C Test. Last accessed online April 29, 2022
National Institute of Diabetes and Kidney and Digestive Diseases. The A1C Test & Diabetes. Last accessed online April 29, 2022
US-OTB-2200090








